Avascular Necrosis Avascular necrosis (AVN) is a disease of the bone. Necrosis is a general term that means a cell has died. AVN is also called:
- Osteonecrosis
- Aseptic necrosis
- Ischemic bone necrosis
- Bone infarction
Grades of AVN There are four stages that define how bad the disease has progressed.
- Stage 1 - has a normal x-rays but MRI reveals the dead bone.
- Stage 2 - can be seen on regular x-ray but there is no collapse of the femoral ball.
- Stage 3- shows signs of collapse.
- Stage 4 - has collapse on x-ray and signs of cartilage
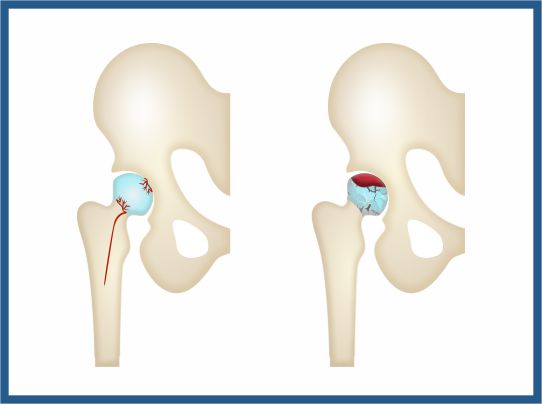
Causes
Osteonecrosis of the hip develops when the blood supply to the femoral head is disrupted. Without adequate nourishment, the bone in the head of the femur dies and gradually collapses.
Risk Factors
- Blood vessels can be damaged even due to the injury to the hip itself.
- Damage to blood vessels can also occur due to fracture of femoral neck.
- Hip dislocation can also cause damage to blood vessels.
- Taking high doses of corticosteroids for a long time, such as prednisone or cortisone, because they can increase fatty substances (lipids) in the blood, which can block arteries
- Smoking and alcohol consumption have been found to cause avascular necrosis. Smoking leads to constriction of blood vessels, thereby reducing the blood flow to hip joint.
- Childhood diseases including Legg-Calve Perthes disease
- Chemotherapy or Radiation
Symptoms
- Mild or severe pain in or around the affected joint
- Groin pain that spreads down to the knee
- Pain that occurs when putting weight on the hip or knee
- Joint pain severe enough to limit movement
- Pain may dramatically increase in intensity because of tiny breaks in the bone, called microfractures. These can cause the bone to collapse.
Treatment
Nonsurgical treatment options
such as anti-inflammatory medications, activity changes, and using crutches.The main objective of the non-surgical treatment is prevention of further damage.
Surgical Option
There are several different surgical procedures used to treat osteonecrosis of the hip.
Core Decompression
This procedure involves drilling one larger hole or several smaller holes into the femoral head to relieve pressure in the bone and create channels for new blood vessels to nourish the affected areas of the hip.
Osteochondral (Bone and Cartilage) Grafting
Core decompression is often combined with bone and cartilage grafting to help regenerate healthy bone and support cartilage at the hip joint. A bone graft is healthy bone tissue that is transplanted to an area of the body where it is needed.
Surgical Treatment
Arthroscopic debridement. This surgery may be helpful in the early stages of arthritis. Debridement (cleansing) is a procedure to remove loose cartilage, inflamed synovial tissue, and bone spurs from around the joint.
Arthrodesis (fusion). Arthrodesis fuses the bones of the joint completely, making one continuous bone out of two or more bones. The goal of the procedure is to reduce pain by eliminating motion in the arthritic joint.
Total ankle replacement (arthroplasty). In total ankle replacement, doctor removes the damaged cartilage and bone, and then positions new metal or plastic joint surfaces to restore the function of the joint.Ankle replacement is most often recommended for patients who have:
Advanced arthritis of the ankle
Arthritis that has destroyed the ankle joint surfaces
Ankle pain that interferes with daily activities
Arthrodesis (fusion). Arthrodesis fuses the bones of the joint completely, making one continuous bone out of two or more bones. The goal of the procedure is to reduce pain by eliminating motion in the arthritic joint.
Total ankle replacement (arthroplasty). In total ankle replacement, doctor removes the damaged cartilage and bone, and then positions new metal or plastic joint surfaces to restore the function of the joint.Ankle replacement is most often recommended for patients who have:
Advanced arthritis of the ankle
Arthritis that has destroyed the ankle joint surfaces
Ankle pain that interferes with daily activities
Vascularized Fibula Graft
In this procedure, a segment of bone is taken from the small bone in your leg (fibula) along with its blood supply (an artery and vein). This graft is transplanted into a hole created in the femoral neck and head, and the artery and vein are reattached to help heal the area of osteonecrosis.
Total Hip Replacement
If osteonecrosis has advanced to the point where the femoral head has already collapsed, the most successful treatment is total hip replacement.
Regenerative Medicine
Minimally invasive autologous adipose-tissue derived stromal vascular fraction (Ad-SVF) has shown a long-term safety and efficacy and has been found as the ideal choice in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the hip.

