Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease. Hip joint is most commonly affected by osteoarthritis.Articular cartilage is the smooth lining, which protects the hip's ball-and-socket joint surfaces. By diminishing friction the cartilage allows joint freedom of movement. The bone layer just beneath the articular cartilage is called subchondral bone. Articular cartilage degeneration occurs in osteoarthritis.
The subchondral bone is exposed and brushes against bone as the articular cartilage degenerates. Small outgrowths in the joint can form, called as bone spurs or osteophytes.
Grade Of Hip Osteoarthritis- 4 Grades of hip OA:
Grade 1- (doubtful OA), possible narrowing of the joint space medially and possible osteophytes around femoral head;
Grade 2 -(mild OA), definite narrowing of the joint space inferiorly, definite osteophytes, and slight sclerosis;
Grade 3 -(moderate OA), marked narrowing of Inter articular space of hip joint
Grade 4-( Severe)
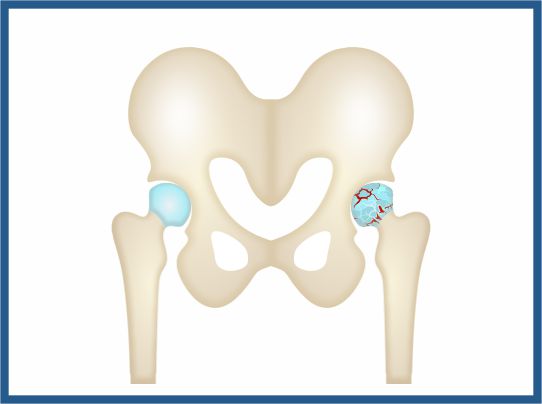
Causes
- Increasing age
- Family history of osteoarthritis
- Previous injury to the hip joint
- Obesity
- Improper formation of the hip joint at birth, a condition known as developmental dysplasia of the hip
Symptoms
- Pain. Affected joints might hurt during or after movement.
- Stiffness. Joint stiffness might be most noticeable upon awakening or after being inactive.
- Tenderness. Joint might feel tender when apply light pressure to or near it.
- Loss of flexibility.
- Grating sensation.
- Bone spurs. These extra bits of bone, which feel like hard lumps, can form around the affected joint.
- Swelling. This might be caused by soft tissue inflammation around the joint.
- Decreased range of motion in the hip that affects the ability to walk and may cause a limp
- Pain that flares up with vigorous activity

